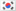
Have you ever noticed the small numbers inside the triangle on plastic products? They’re not just random designs; they carry important information about the type of plastic and its safety level. Let’s explore the 7 most common plastic symbols and how to differentiate them to protect yourself and your family’s health!

Why should we care about plastic symbols?
Plastic is a convenient material widely used in our daily lives. However, not all plastics are safe. Some types of plastic, when exposed to high temperatures or used to store food, can release harmful chemicals that affect our health. Understanding plastic symbols helps you:
– Choose safe products: Avoid using plastic products that can harm your health, especially when storing food or hot beverages.
– Recycle properly: Each type of plastic has its own recycling process. Sorting plastics by symbol makes recycling more efficient.
– Protect the environment: Reduce the amount of plastic waste and contribute to protecting the planet.

The 7 most common plastic symbols
1. PET or PETE (Number 1): Commonly used for producing water bottles and carbonated beverage bottles. Avoid reusing multiple times and avoid exposure to high temperatures.

2. HDPE (Number 2): A hard, durable plastic often used for milk bottles, oil bottles, and detergents. This type of plastic is relatively safe and can be recycled multiple times.
3. PVC (Number 3): A soft, flexible plastic commonly used for producing pipes and food wraps. Contains harmful chemicals and should not be used for storing food or beverages.

4. LDPE (Number 4): A soft, flexible plastic often used for producing plastic bags and food wraps. Should not be used in microwaves or at high temperatures.

5. PP (Number 5): A hard, durable, heat-resistant plastic often used for producing food containers and straws. This type of plastic is relatively safe and can be recycled multiple times.

6. PS (Number 6): A hard, brittle plastic often used for producing fast food containers and paper cups. Should not be used for storing hot food or acidic beverages.

7. Other (Number 7): This category includes other types of plastics that don’t fall into the above categories. The most common plastics in this category are PC (Polycarbonate) and Tritan. Among these, Tritan, a naturally derived plastic, is considered the safest.

Many people often confuse Tritan with PC, but these two types are completely different and should be distinguished as follows:
– PC (Polycarbonate): While a good type of plastic, PC still contains BPA and cannot be recycled. It is clear and hard, and can break easily when dropped. The bottom of the container is marked with number 7, but the body does not have the label “BPA Free” (or “BPA-free”).
– Tritan: This is a natural plastic, marked with number 7 at the bottom and “BPA Free Tritan” (or “BPA-free”) on the body. It has the clarity of glass, is less likely to break when dropped, and is exceptionally safe for users, especially when used for sports water bottles.

Which plastic is the safest?

HDPE (number 2), PP (number 5), and Tritan (number 7) are generally considered the safest types of plastics. They are highly durable, heat-resistant, and release fewer harmful chemicals.
Additionally, PETE (number 1) and LDPE (number 4) are also considered safe for food storage, but they should not be recycled multiple times and should be avoided from high temperatures.
PVC (number 3), PS (number 6), and PC (number 7) are types of plastics that should not be used for food storage. However, to ensure absolute safety, it is recommended to limit the use of plastic products, especially when storing food or beverages.
Some notes on using plastic products
– Do not use scratched or deformed plastic products.
– Do not heat food in plastic containers in the microwave unless clearly indicated.
– Do not reuse plastic bottles multiple times.
– Recycle plastic properly to protect the environment.