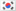
The Lily: A Symbol of Purity and Eternal Life
The lily, a flower renowned for its pristine beauty and enduring symbolism, has long held a special place in cultures worldwide. From the vast fields of lilies in the Netherlands to the delicate blooms depicted in famous paintings, this flower has captivated flower enthusiasts for centuries.
Belonging to the Lilium genus, lilies are also known as Bách hợp or Huệ tây. They are celebrated for their intoxicating fragrance, diverse colors, and numerous varieties.
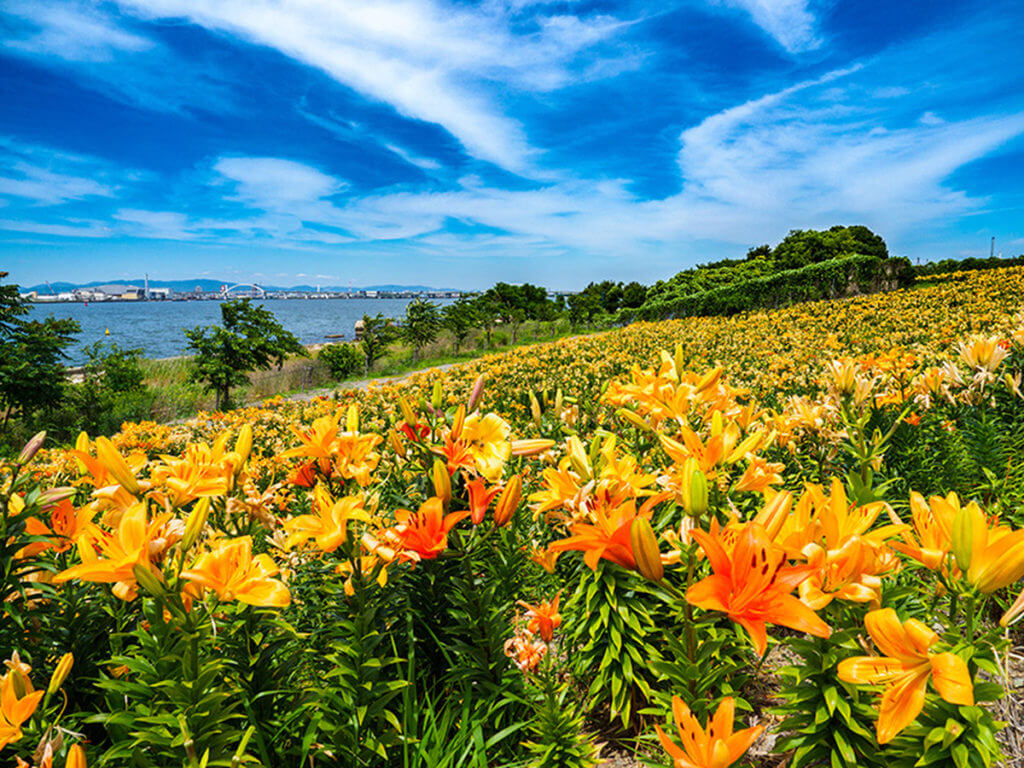

In Western cultures, lilies symbolize purity and are often considered sacred. They are also seen as emblems of power, prosperity, victory, nobility, and elegance. Furthermore, lilies represent willpower, aspirations, growth, and the bonds of love and happiness, mirroring their Vietnamese name, Bách hợp.
In Feng Shui, lilies are believed to bring good fortune and ward off evil spirits. As a result, they are commonly placed in homes during the Lunar New Year and other important celebrations.
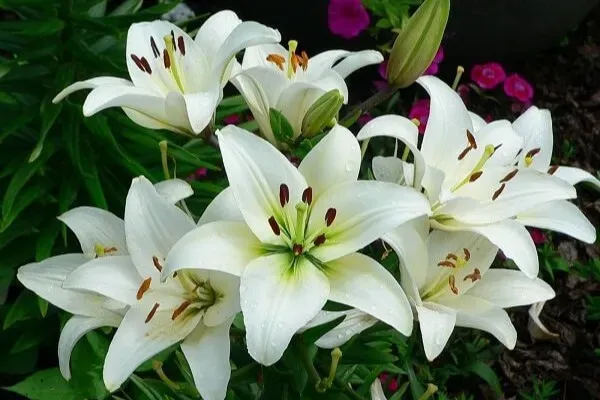

There are approximately 80-100 lily species distributed across the globe. In Vietnam, popular varieties include Longiflorum (LA), Oriental (OR), and Asiatic. Other well-known varieties worldwide include Daylily, Tiger Lily, Aurelian, Asiatic, Trumpet, and Candidum, which come in a wide range of colors such as white, orange, pink, purple, red, and yellow.
1. Planting Season
As a temperate climate plant, lilies thrive in cool environments. In northern Vietnam, the ideal planting time is around late September (lunar calendar) to ensure flowering for the Lunar New Year. However, adjust the planting time based on the annual weather conditions.

2. Pre-planting Preparations
2.1. Growing Medium
Use a well-draining, nutrient-rich potting mix. A mixture of garden soil, coir coir, husk charcoal, and vermicompost in a 3:2:2:3 ratio is suitable. Add a beneficial fungus to prevent diseases.
2.2. Bulb Selection
The diverse world of lilies offers a wide range of varieties, each with its own unique growth timeline that can fluctuate between 65 and 100 days. Understanding this variation is key to cultivating these beautiful blooms.
Choose plump, healthy bulbs without any signs of pests or diseases. Larger bulbs with a circumference of 16-20 cm or more have a higher germination rate.

2.3. Pot Selection
Use plastic or clay pots with a minimum diameter of 22 cm for 3 bulbs or 32 cm for 5 bulbs.
Elevate the pot to improve drainage.




3. Planting Lily Bulbs
3.1. Pre-planting Disease Treatment
Before planting, mix Benkona and Carbendazim fungicides according to the recommended ratio on the package. Soak the bulbs in this solution for 10-15 minutes to eliminate any diseases. Then, remove the bulbs, let them dry, and plant them.
3.2. Planting Lilies in Pots
t’s best to plant lilies on cool days. Fill the pot halfway with the prepared potting mix. Gently place the bulb in the center, ensuring the sprout faces upwards.
Cover the bulb completely with the remaining potting mix and lightly press down to secure it. Place the pot in a cool, shaded area, away from direct sunlight. Apply a root-stimulating solution 3-4 times, with 5-7 days between each application.

For the first week after planting, keep the soil consistently moist. Use a gentle watering can or a fine mist spray to avoid disturbing the delicate young plants. After about 10-12 days, you should start to see new roots developing.
4. Caring for Lilies
To ensure your potted lilies grow healthily and produce large, beautiful, fragrant blooms, pay attention to the following care tips:
4.1. Temperature and Humidity
Lilies are fairly cold-tolerant but do not tolerate heat well. They thrive in cool, humid conditions. The ideal daytime temperature is 20-28°C and nighttime temperature is 12-20°C. Temperatures below 12°C can hinder growth and cause bud drop. Lilies prefer high humidity levels, ideally between 80% and 85%.
4.2. Light
Lilies prefer moderate light. You can shade them by 50-70% using a shade net placed 2-2.5 meters away from the pots. After 15-20 days, remove the shade net. On hot days, you may need to reapply the shade net.
After 35-45 days of planting, provide supplemental lighting for 3 hours daily (from 6 PM to 9 PM). Lilies require long day lengths to induce flowering, so continuous supplemental lighting for 20 days is recommended.
Insufficient light can cause the production of ethylene, a hormone that can lead to bud drop or malformed buds, as lilies are quite sensitive to ethylene.

4.3. Watering
Maintaining consistent soil moisture is crucial throughout the growing process. Young plants require more water, while flowering plants need less. Water gently at the base of the plant, avoiding wetting the leaves and buds to prevent bud drop and bulb rot.
The amount of water needed depends on factors such as soil type, air temperature, and plant growth. It’s best to water before 10 AM.
4.4. Fertilizing
tart fertilizing 15-20 days after planting. Use organic fertilizers like vermicompost or goat manure in combination with NPK 20-20-15 or NPK 16-16-8. Apply fertilizer every 7-10 days. After 40-45 days, supplement with foliar fertilizers high in phosphorus and potassium, such as NPK 6-30-30, NPK 15-30-15,… Apply foliar fertilizers every 7-10 days.
4.5. Pest and Disease Control
Lilies are often susceptible to aphids, especially when they are in bloom. The fragrance of the flowers attracts aphids, which can cause stunted growth, distorted leaves, and bud blight.

To keep aphids away, feed your lilies well and make sure they get enough water. Natural pest control options like Neem oil and mineral oil can help. If you see aphids, try spraying them off with a strong jet of water. For stubborn infestations, use a specific insecticide like Movento or Confidor.
Lily bulbs can rot or develop scale, causing your plant to look unhealthy. Look for brown spots on the bulbs or near the base of the plant. If you see these spots, treat the plants with a fungicide like Ridomil Gold or Aliette. If the problem is severe, remove the affected plants to prevent the disease from spreading.
4.6. Harvesting potted lilies
After 50-55 days of planting, lily buds will form. The flowers will bloom about 15-20 days later.
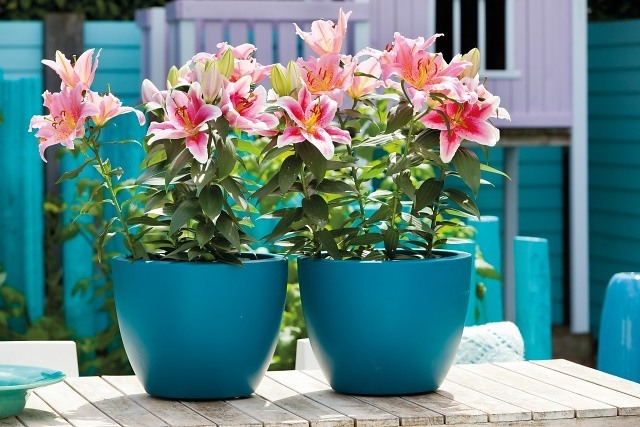

The optimal time to cut the flowers is when the lower part of the bud swells and the two bottom buds change color.
It’s best to cut the flowers early in the morning or late in the afternoon, avoiding midday or hot weather. Water the plants about an hour before cutting to ensure the flowers are well-hydrated.
Cut the stems about 10-15 cm above the ground to allow the bulb to continue growing. Leave 5-6 leaves on each stem after cutting.