Gardening in raised beds offers a fantastic way to cultivate high-efficiency plants, making the most of limited space while promoting healthier growth. Whether you’re new to raised bed gardening or looking to optimize your current setup, the right techniques can boost your harvest and simplify the process
1. Choose the ideal location
.jpg)
Take a walk around your backyard and note where the sun shines at various times throughout the day. Since most fruits, vegetables, and herbs need plenty of sunlight to grow well, aim to position your raised bed in an area that gets at least 6 hours of direct sunlight. If you live in a hot climate, it’s also a good idea to select a spot that offers shade or relief from the strong afternoon sun to protect your plants from overheating.
2. Choose suitable plants to grow
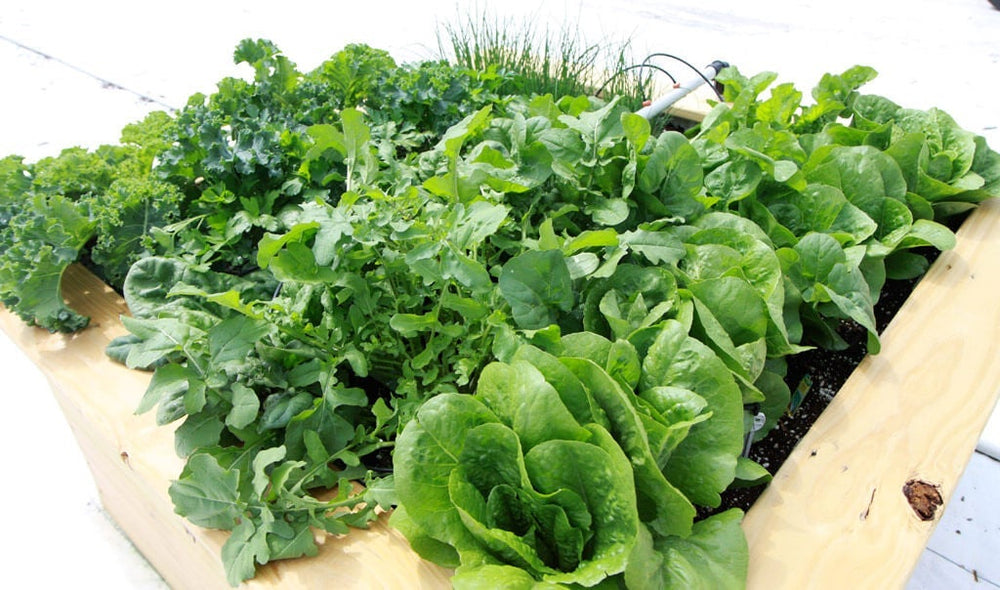

Raised garden beds offer excellent drainage, making them ideal for crops with shallow roots that are susceptible to rot in waterlogged soil. Leafy greens such as lettuce, spinach, kale, and swiss chard are great choices, as they are low-maintenance and thrive in these conditions. Alternatively, you can grow tomatoes, peppers, eggplants, and pole beans in these beds as well.
To attract pollinators while adding some vibrant color, consider planting flowers like marigolds, zinnias, cosmos, or sunflowers. If you’re more interested in herbs, options like roses, lavender, basil, and chives will flourish in soil that’s kept moist but not overly wet.
3. Start with quality soil :strip_icc()/bhg-raised-garden-beds-apr-24-test-vego-kits-laura-miller-025-392cb0d89020499fa5f2b9218c4fcbc7.jpeg)
The key to a thriving raised bed is ensuring your soil is in optimal condition. Soil from your yard or garden is often too compacted for use in raised beds or pots. For best results, you’ll want to combine potting mix with garden soil. Raised beds, whether deep or shallow, offer the opportunity to tailor soil conditions to suit your plants on a larger scale. While the potting mix alone is too airy for raised beds, a 50:50 mix of potting soil and garden soil provides the perfect balance for healthy plant growth.
4. Don’t overcrowd plants

While it’s easy to get excited and plant as many vegetables as you can in a raised bed, overcrowding can hinder growth, spread diseases, and reduce your harvest. Plants require adequate space to grow, and when too crowded, they compete for sunlight, water, and nutrients. To avoid this, plan your garden with proper spacing between plants based on their individual requirements. Additionally, incorporating companion planting can help you make the most of your space by pairing plants that support each other’s growth.
5. Use organic straw and shredded leaves as mulch

Organic straw is an ideal mulch for raised beds. It’s easy to spread and typically decomposes within a year. Straw blocks sunlight, preventing weed growth, while helping to regulate soil temperature—keeping it cooler in hot weather and warmer during colder months.
Shredded leaves also make great mulch for raised beds. They are abundant, inexpensive, and offer similar benefits to straw.